Sunderland Classification | This classification scheme combines multiple types of nerve injuries seen in the sunderland 2.4 nerve injury classification via independent classification. Nerve injuries as discussed previously. Download scientific diagram | seddon and sunderland classification of nerve injuries from publication: Sunderland classification of nerve injury has 5 degrees: Nerve contusion or stretch leading to reversible conduction block without wallerian degeneration.
The seddon classification is useful to understand the anatomic basis for injury, while the sunderland classification adds information useful for prognosis and treatment strategies. There is similarity between the two systems, with sunderland's offering greater detail of description. Axon, endoneurium and perineurium damaged with intact epineurium a. Sunderland classification of nerve injury. There are three basic types of peripheral nerve injuries (pni) commonly seen in the clinic.
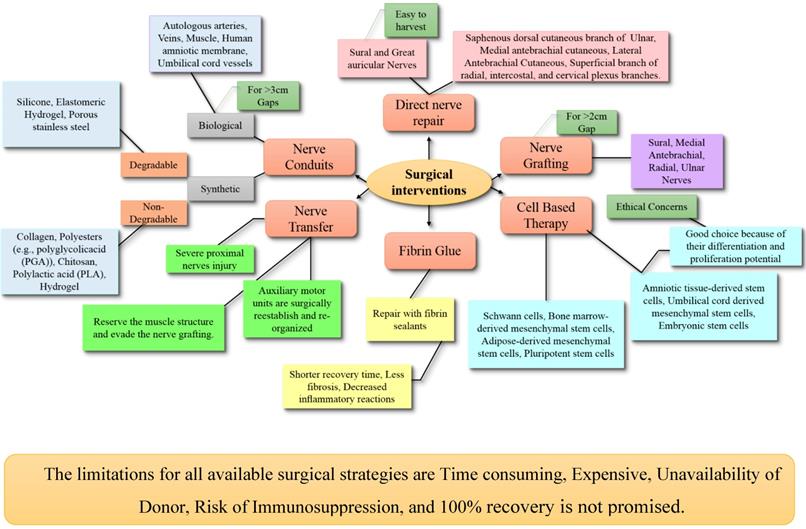
The most widely used classification of nerve injuries are seddon & sunderland. Sunderland's classification specifies five degrees of nerve damage. Axon, endoneurium and perineurium damaged with intact epineurium a. Current status of therapeutic approaches against peripheral nerve injuries. 63 the first degree corresponds to neurapraxia in seddon's schema; A classification system called the sunderland classification system defines five different degrees of peripheral nerve injury Nerve injuries were classified by seddon in 1943 and expanded by sunderland in 1951. This classification scheme combines multiple types of nerve injuries seen in the sunderland 2.4 nerve injury classification via independent classification. Sunderland, a classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function, brain, vol. The second corresponds to axonotmesis; Learn more on this topic. As referenced to seddon and sunderland classifications. Sunderland classification of nerve injury.
This classification scheme combines multiple types of nerve injuries seen in the sunderland 2.4 nerve injury classification via independent classification. Sunderland, a classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function, brain, vol. Understanding nerve injury classification is essential for prognostic value clinically. In 1953, sunderland expanded seddon's classification from three to five degrees of peripheral nerve injury. Seddon classification classifies nerve injuries as neuropraxias axonotmesis or neurotmesis.1 sunderland classification basis the injury on level of anatomic injury.
As referenced to seddon and sunderland classifications. Seddon classification of nerve injuries (in 1941) In 1953, sunderland expanded seddon's classification from three to five degrees of peripheral nerve injury. A classification system called the sunderland classification system defines five different degrees of peripheral nerve injury The seddon classification is useful to understand the anatomic basis for injury, while the sunderland classification adds information useful for prognosis and treatment strategies. Peripheral nerve injury grading simplified on mr neurography: The sunderland classification is based on the degree of tissue injury (sunderland, 1978). The injuries are arranged in ascending order of severity from the. Nerve injuries were classified by seddon in 1943 and expanded by sunderland in 1951. Consists of 5 degrees of injury (further stratifying the extent of endo/peri/epineurium. Sunderland classification of nerve injury. An online course by wendy walker. Understanding nerve injury classification is essential for prognostic value clinically.
Nerve injuries were classified by seddon in 1943 and expanded by sunderland in 1951. Seddon classification classifies nerve injuries as neuropraxias axonotmesis or neurotmesis.1 sunderland classification basis the injury on level of anatomic injury. Sunderland classification of nerve injury has 5 degrees: The most widely used classification of nerve injuries are seddon & sunderland. Nerve contusion or stretch leading to reversible conduction block without wallerian degeneration.
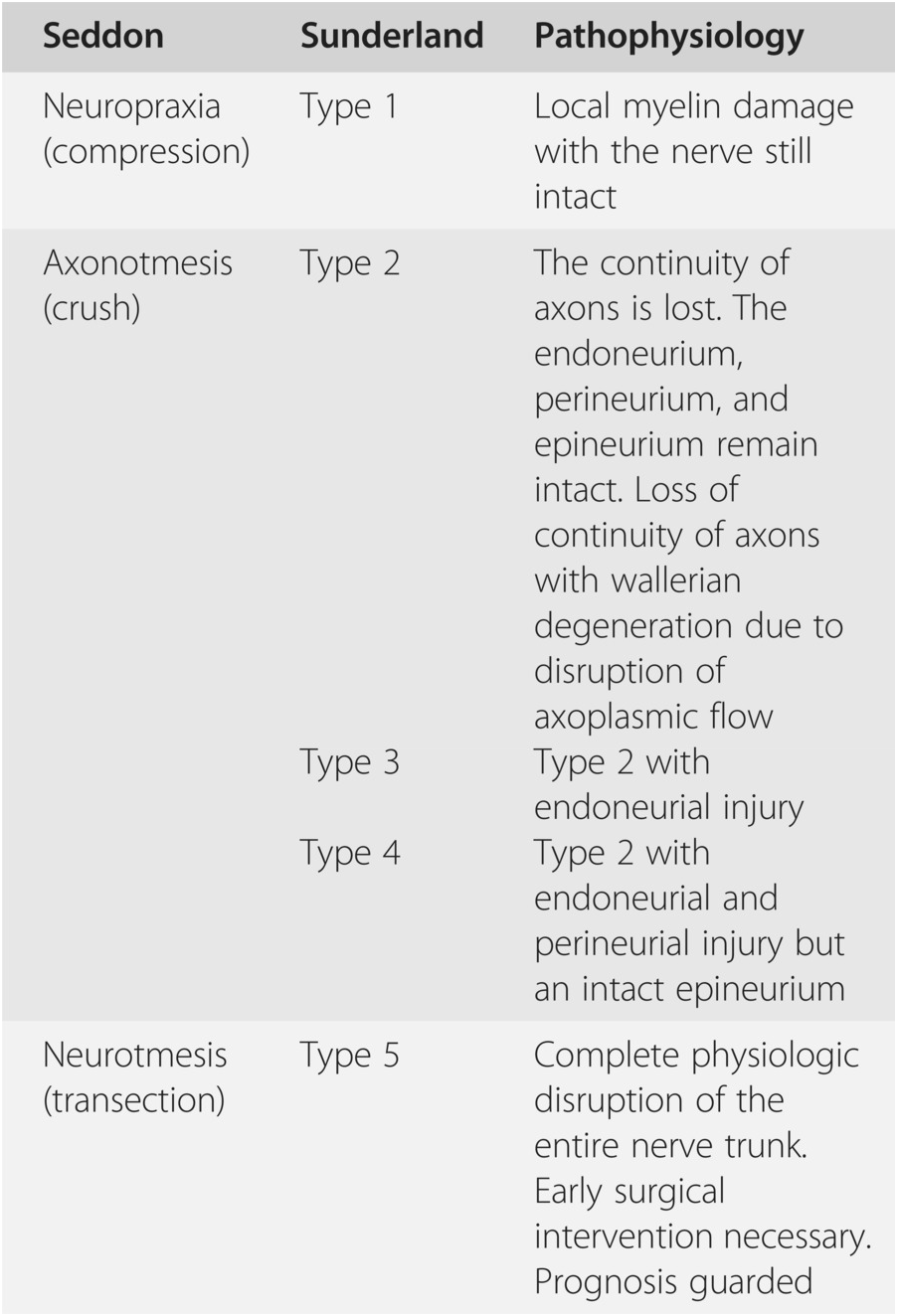
This classification scheme combines multiple types of nerve injuries seen in the sunderland 2.4 nerve injury classification via independent classification. Learn more on this topic. The sunderland classification is based on the degree of tissue injury (sunderland, 1978). Sunderland classification of nerve injury has 5 degrees: Sunderland's classification specifies five degrees of nerve damage. Consists of 5 degrees of injury (further stratifying the extent of endo/peri/epineurium. Sunderland, a classification of peripheral nerve injuries producing loss of function, brain, vol. As referenced to seddon and sunderland classifications. Understanding nerve injury classification is essential for prognostic value clinically. Axon, endoneurium and perineurium damaged with intact epineurium a. Nerve contusion or stretch leading to reversible conduction block without wallerian degeneration. 63 the first degree corresponds to neurapraxia in seddon's schema; An online course by wendy walker.
Current status of therapeutic approaches against peripheral nerve injuries sunderland. Seddon classification of nerve injuries (in 1941)
Sunderland Classification: There is similarity between the two systems, with sunderland's offering greater detail of description.
Source: Sunderland Classification
EmoticonEmoticon